|
The transition to 800V EVs affects the entire powertrain, including the power electronics. The automotive industry is increasingly adopting 800V platforms for battery electric vehicles (BEVs). While 400V systems will remain relevant in the coming decade, the performance and efficiency benefits of 800V architectures are compelling and, in most cases, justify the required powertrain re-engineering. This new release, written by industry expert John Li, a technology analyst at market intelligence firm IDTechEx, explains the advantages of 800V platforms and how the transition is being achieved. For additional expert commentary around this topic, please reach out to press@IDTechEx.com. --- For Immediate Release IDTechEx Assesses the Current Status of 800V for EVs Monday 15th December 2025 IDTechEx Cambridge, UK IDTechEx Assesses the Current Status of 800V for EVs The transition to 800V EVs is one which affects the whole powertrain, including the power electronics. In IDTechEx’s report, Power Electronics for Electric Vehicles 2026-2036: Technologies, Markets, and Forecasts, these trends are analysed and used to forecast the adoption of wide bandgap semiconductors SiC and GaN, as well as the entire power electronics market for electric vehicles (EV). 800V is Mature and Proven The automotive industry is converging on 800V platforms for battery electric vehicles (BEVs), when earlier generations of vehicle were 400V. While 400V will certainly have a part to play in the next decade, the advantages of 800V platforms are undeniable, and in most cases worth the re-engineering of the powertrain to accommodate this. Firstly, the higher voltage means that the battery can charge at greater power while using less current. For consumers that want charging to be as quick as refueling an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle, 800V vehicles can deliver greater average and peak rates of power. While this is generally the case, other parameters in the vehicle and also in the charger will determine the actual charging speed. Secondly, since the voltage is much higher, significantly less current is required to deliver the same amount of power to the traction inverter and the motor. The end result is fewer losses and greater efficiency, allowing for either a small increase in range, or a reduction in battery size (and therefore weight and cost). Either case is advantageous, and SiC MOSFETs are much more efficient than Si IGBTs at 800V due to its material and device properties, such that the transition to 800V EVs and SiC MOSFETs go hand in hand. Finally, since less current runs through the wiring harnesses in the vehicle, the diameter of the wiring harness can be significantly reduced. Copper is heavy and expensive, so a theoretical halving of the wiring harness diameter (excluding insulation and cooling requirements) delivers a compounded cost and weight saving. Even though BEVs are much more efficient than ICE vehicles, squeezing out extra efficiency at lower cost is beneficial to the consumer, but also to the OEM, many of which have struggled with the profitability of their BEVs. There Are Different Ways to Achieve 400V to 800V Compatibility
There is one glaring issue with building an 800V platform EV: the majority of DC chargers in the world are 400V, meaning that there needs to be an onboard system to convert the 400V DC from the charger to 800V DC to charge the high voltage battery. Without such a system, the majority of DC chargers cannot be used. Mercedes controversially did not include an 800V booster in its announcement for the Mercedes CLA EV earlier in 2025, although this has since been reversed. IDTechEx has identified three key ways to achieve 400V to 800V charging compatibility, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. While each system is complex, IDTechEx has found that battery switching, DC boost converters, and traction integrated onboard chargers are the three main approaches from OEMs and tier-one suppliers to achieve 800V compatibility. Boost converters are the simplest method, whereby an extra DC-DC converter is installed onto the vehicle to boost the voltage from 400V to 800V before feeding into the high voltage battery. While this is simple, it is also costly to add this extra unit, especially when space in a vehicle is limited to begin with. This is the method used in the Porsche Taycan. By switching the configuration of cells in charging, the battery pack can be charged as a mix of series and parallel connections to match the incoming voltage from the DC charger. The GMC Hummer and Tesla Cybertruck run variants of this technique to ensure charging compatibility. Finally, traction integrated onboard chargers are a unique way to boost the voltage without the need for a separate DC-DC converter. The windings in the electric motor act as filter inductance, and are used to boost the voltage of the incoming DC from the charger without requiring a separate DC-DC converter unit. This is the approach used by Hyundai and Kia, and multiple tier-one suppliers have similar methods to boost voltage. 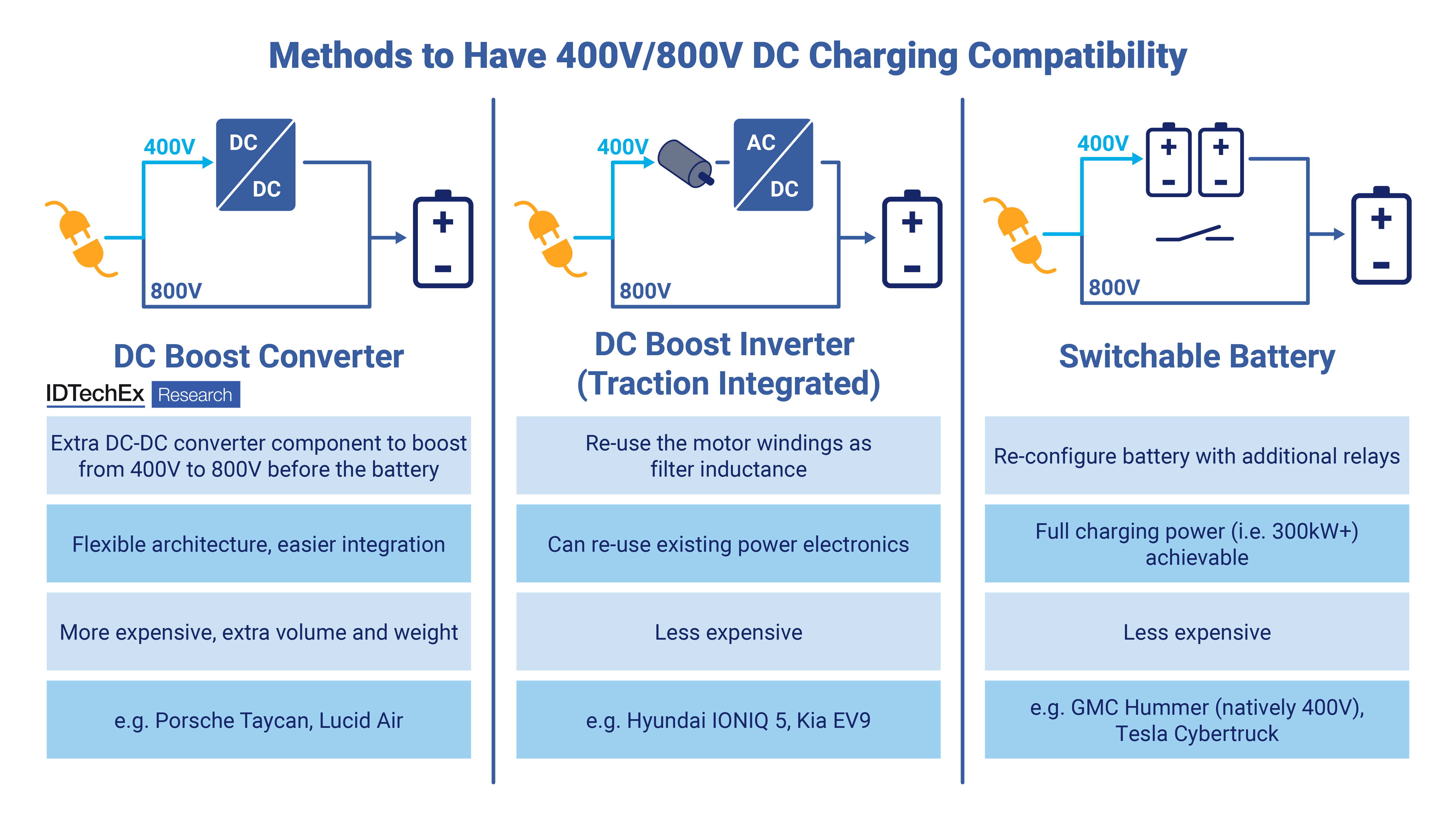
IDTechEx compares the three different ways to have charging compatibility between 400V and 800V. Source: IDTechEx. IDTechEx analyzes different power electronics innovations alongside semiconductor technologies to forecast what the market will look like in ten years. Further information can be found in IDTechEx’s report, Power Electronics for Electric Vehicles 2026-2036: Technologies, Markets, and Forecasts. For more information on this report, including downloadable sample pages, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/PowerElec, or for the full portfolio of EV research available from IDTechEx, see www.IDTechEx.com/Research/EV. About IDTechEx
IDTechEx provides trusted independent research on emerging technologies and their markets. Since 1999, we have been helping our clients to understand new technologies, their supply chains, market requirements, opportunities and forecasts. For more information, contact research@IDTechEx.com or visit www.IDTechEx.com. Media Contact:
Charlotte Martin
Subscriptions Marketing Manager press@IDTechEx.com
+44(0)1223 812300
|